The Importance of Cooling Systems in High-Performance PCs
Iren
- 0
- 994
Understanding PC Cooling
Cooling systems are an integral part of high-performance PCs, playing a crucial role in maintaining optimal performance and extending the lifespan of computer components. As modern processors and graphics cards become more powerful, they also generate more heat, making efficient cooling solutions essential for stable operation and preventing thermal damage.
Air Cooling Systems
Air cooling is the most common and cost-effective method of heat dissipation in PCs. It relies on heatsinks and fans to transfer heat away from components and expel it from the case.
Key components of air cooling systems:
- Heatsinks: Metal structures with high thermal conductivity
- Fans: Push or pull air across the heatsink fins
- Thermal paste: Enhances heat transfer between the component and heatsink
Pros and cons of air cooling:
|
Pros |
Cons |
|---|---|
|
Cost-effective |
Limited cooling capacity |
|
Easy to install and maintain |
Can be noisy at high speeds |
|
No risk of leaks |
Takes up more space in the case |
|
Reliable and long-lasting |
Less efficient for extreme overclocking |
Liquid Cooling Systems
Liquid cooling systems use a coolant to absorb and transfer heat from components more efficiently than air. These systems can be either closed-loop (All-In-One) or custom-loop configurations.
Components of a liquid cooling system:
- Pump: Circulates the coolant
- Radiator: Dissipates heat from the coolant
- Tubing: Transports the coolant
- Waterblocks: Transfers heat from components to the coolant
- Coolant: Liquid medium for heat transfer (usually a mix of distilled water and additives)
Comparison of liquid cooling vs. air cooling:
|
Factor |
Liquid Cooling |
Air Cooling |
|---|---|---|
|
Cooling efficiency |
Higher |
Lower |
|
Noise levels |
Generally quieter |
Can be louder |
|
Cost |
More expensive |
More affordable |
|
Installation complexity |
More complex |
Simpler |
|
Maintenance |
Requires periodic maintenance |
Minimal maintenance |
|
Risk of leaks |
Present |
None |
The Role of Cooling in PC Performance
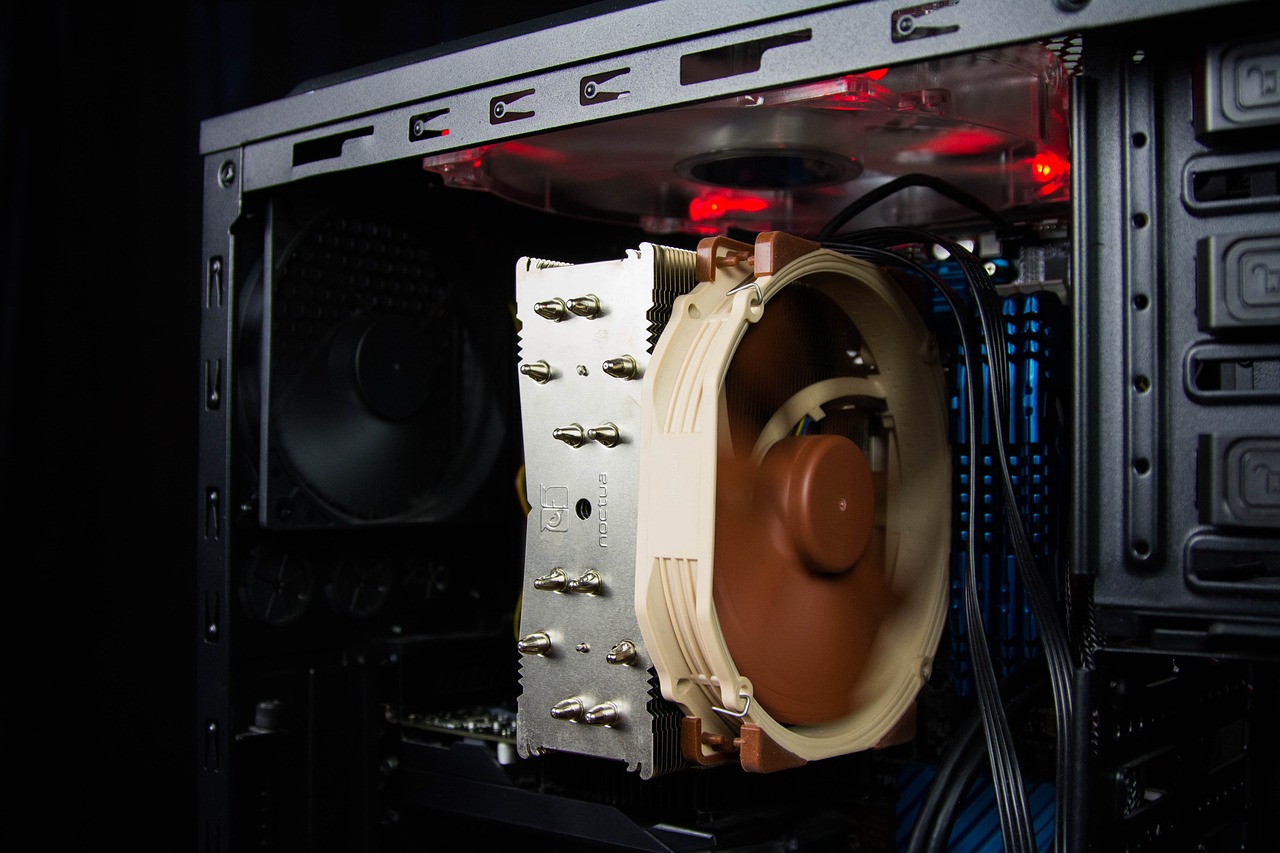

Effective cooling systems are crucial for maintaining optimal PC performance, especially in high-performance setups.
Preventing Thermal Throttling
Thermal throttling is a protective mechanism that reduces CPU or GPU clock speeds when temperatures reach critical levels. This process helps prevent damage to components but results in decreased performance.
Examples of thermal throttling impacts:
- FPS drops in gaming during intense scenes
- Slower render times in video editing
- Reduced processing speed in data analysis tasks
By implementing efficient cooling solutions, users can prevent thermal throttling and maintain consistent performance across various workloads.
Overclocking and Cooling
Overclocking involves pushing components beyond their stock speeds to achieve higher performance. This process generates additional heat, making advanced cooling solutions essential.
Relationship between overclocking and cooling:
- Higher clock speeds increase power consumption
- Increased power consumption leads to more heat generation
- Advanced cooling is required to dissipate the extra heat
- Better cooling allows for higher and more stable overclocks
Enthusiasts often opt for high-end air coolers or liquid cooling systems to support their overclocking endeavors and maintain safe operating temperatures.
Types of Cooling Systems
High-Performance Air Coolers
High-performance air coolers offer improved cooling capacity over stock solutions, making them suitable for moderately overclocked systems.
Features of high-end air coolers:
- Large heatsinks with multiple heat pipes
- High-quality fans with PWM control
- Advanced fin designs for improved airflow
- Compatibility with various CPU sockets
Example: Be Quiet! PURE ROCK 2 FX ARGB
- 150W TDP cooling capacity
- Four 6mm heat pipes
- 120mm PWM fan with ARGB lighting
- Asymmetric design for improved RAM clearance
Liquid Cooling Systems
Liquid cooling systems offer superior heat dissipation compared to air cooling, making them ideal for high-performance and overclocked setups.
Types of liquid cooling systems:
- All-In-One (AIO) coolers
- Custom loop systems
Comparison of liquid cooling solutions:
|
Factor |
AIO Coolers |
Custom Loop |
|---|---|---|
|
Ease of installation |
Simpler |
Complex |
|
Customization |
Limited |
Highly customizable |
|
Maintenance |
Minimal |
Regular maintenance required |
|
Cooling capacity |
Good |
Excellent |
|
Cost |
Moderate |
High |
|
Expandability |
Fixed |
Expandable to cool multiple components |
Advanced Cooling Techniques

For enthusiasts and extreme overclockers, advanced cooling techniques offer even greater thermal management capabilities.
Phase Change Cooling
Phase change cooling uses the principle of refrigeration to achieve sub-zero temperatures for extreme overclocking.
How phase change cooling works:
- Compressor circulates refrigerant through the system
- Refrigerant evaporates in the evaporator, absorbing heat from the CPU
- Compressor pressurizes the refrigerant vapor
- Condenser releases heat and liquefies the refrigerant
- Process repeats, maintaining sub-zero temperatures
Benefits and drawbacks of phase change cooling:
|
Benefits |
Drawbacks |
|---|---|
|
Extreme low temperatures |
High power consumption |
|
Enables extreme overclocking |
Expensive |
|
Eliminates thermal throttling |
Large and noisy |
|
Consistent performance |
Risk of condensation |
Submersion Cooling
Submersion cooling involves immersing computer components in non-conductive fluids for efficient heat dissipation.
Types of submersion cooling:
- Mineral oil submersion
- Engineered dielectric fluids (e.g., 3M Novec)
Applications of submersion cooling:
- Data centers for improved energy efficiency
- Overclocking competitions for extreme cooling
- Specialized industrial computing environments
While not practical for most users, submersion cooling offers unparalleled thermal management for specific use cases.
Maintenance and Optimization
Proper maintenance and optimization of cooling systems are essential for long-term performance and reliability.
Regular Cleaning and Maintenance
Dust accumulation can significantly impact cooling efficiency. Regular cleaning helps maintain optimal airflow and heat dissipation.
Maintenance checklist:
- Clean dust filters monthly
- Remove dust from fan blades and heatsinks quarterly
- Replace thermal paste every 2-3 years
- Check and tighten liquid cooling fittings annually
- Inspect fans for signs of wear and replace if necessary
Optimizing Airflow
Proper airflow management within the PC case is crucial for effective cooling.
Tips for optimizing airflow:
- Follow the front-to-back airflow principle
- Use positive air pressure (more intake than exhaust fans)
- Minimize cable clutter to reduce airflow obstruction
- Consider using fan splitters or controllers for better management
- Place the PC in a well-ventilated area
Future Trends in PC Cooling
As technology advances, new cooling solutions are emerging to meet the demands of increasingly powerful hardware.
AI-Driven Cooling Systems
Artificial Intelligence is being integrated into cooling systems to optimize performance dynamically.
Features of AI-driven cooling:
- Real-time temperature and load monitoring
- Predictive fan speed adjustments
- Adaptive overclocking based on thermal headroom
- Integration with system-wide power management
For example, the NZXT Kraken Z-3 series AIO coolers feature AI-powered fan control for optimal cooling performance.
Eco-Friendly Cooling Solutions
As environmental concerns grow, manufacturers are developing more sustainable cooling solutions.
Eco-friendly cooling innovations:
- Biodegradable coolants for liquid cooling systems
- Energy-efficient fan designs
- Use of recycled materials in cooler construction
- Heat recycling systems for data centers
These developments aim to reduce the environmental impact of high-performance computing while maintaining effective cooling capabilities.
Conclusion
Cooling systems play a vital role in the performance, stability, and longevity of high-performance PCs. From basic air cooling to advanced liquid and phase change solutions, proper thermal management is essential for unleashing the full potential of modern hardware. As technology continues to evolve, so too will cooling solutions, driven by the need for greater efficiency, performance, and environmental sustainability. By understanding and implementing effective cooling strategies, PC enthusiasts can ensure their systems operate at peak performance while maintaining safe temperatures and prolonging component lifespan.